

- REDSHIFT ALTER TABLE COLUMN TYPE HOW TO
- REDSHIFT ALTER TABLE COLUMN TYPE GENERATOR
- REDSHIFT ALTER TABLE COLUMN TYPE PLUS
However, the same documentation states that these are informational only and are not enforced. Redshift does support creation of unique, primary key and foreign key indexes (referred to in the Redshift Documentation as constraints).
REDSHIFT ALTER TABLE COLUMN TYPE HOW TO
Instead, you choose distribution styles and sort keys when you follow recommended practices in How to Use DISTKEY, SORTKEY and Define Column Compression Encoding in Redshift. It does not support regular indexes usually used in other databases to make queries perform better. For more information, refer to the Identity Columns section.Being a columnar database specifically made for data warehousing, Redshift has a different treatment when it comes to indexes. By the use of this command, you can also "reset" the number generator.
REDSHIFT ALTER TABLE COLUMN TYPE PLUS
Starting with the number specified plus one, monotonically increasing numbers are generated for INSERT statements, which do not insert an explicit value to the identity column.
REDSHIFT ALTER TABLE COLUMN TYPE GENERATOR
When specifying the optional parameter int, the number generator will be set to this number.The contents of the table is not affected by this statement.DROP DEFAULT should be given priority over SET DEFAULT NULL.For information on the permissible expression for default value expr, refer to the Default Values section.A default value must be convertible to the data type.This statement will not change the contents of the table.If the column that is modified is a part of the distribution key (see ALTER TABLE (Distribution/Partitioning) for more information), then the table is redistributed.If you do not specify a constraint, then existing constraints are not changed. However, the only exception is when you specify a NULL constraint, a previously existing NOT NULL constraint is removed. By specifying constraints in the MODIFY command, you can only add constraints, but not modify them.For more information, refer to the Identity Columns sections. However, the data type of the modified column should be appropriate else an error is displayed. When you modify an identity column and do not specify the modified column as an identity column, then the modified column still retains the identity column property.For information on the permissible expression for default value expr, refer to the Default Values section. If a default value is not specified, then any old default value that exists and which is appropriate to the new data type will be used.
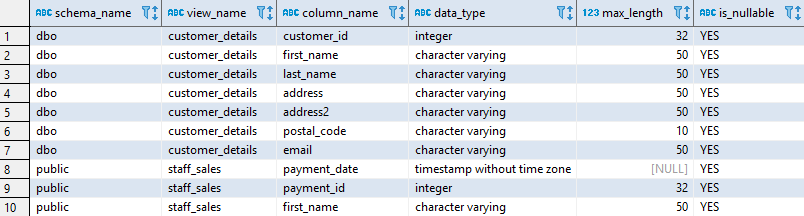
For example, in data types, BOOL cannot be converted to TIMESTAMP, and for the content of a column, if you have CHAR (3) with the content '123', then it can be converted to DECIMAL, however, if the content is 'ABC', it cannot be converted.Ī default value must be convertible to the data type.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
